Lung Cancer Mainly Affects Women
Lung cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer among women and, in fact, the most deadly of all breast and uterine cancers.
Women are increasingly exposed to toxic substances in the environment and, unfortunately, the number of smokers is increasing considerably.
According to statistics, women who have smoked for more than 10 years have more than a 50% chance of contracting lung cancer.
Furthermore, women’s lungs deteriorate prematurely, making them vulnerable to developing severe respiratory diseases.
Although many don’t know it, lung cancer is the most common leading cause of death among men and women.
Misinformation about the disease and constant exposure to factors that determine its development play a fundamental role in the tragic consequences.
Lung cancer in the female population
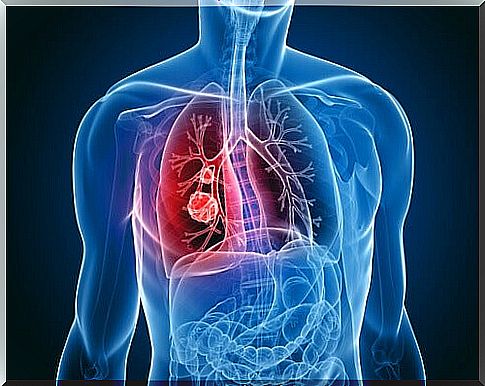
A study conducted by the American Cancer Society and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) revealed that lung cancer is lethal to women in developed countries.
Researchers believe that the increase in the number of smokers is an important fact to demonstrate these results.
“The smoking epidemic,” as experts call it, has spread significantly among consumers and, in some countries, female smokers outnumber men who smoke.
It is estimated that more than 80% of positive diagnoses in women are a consequence of smoking, while the remaining 20% depend on other lung problems, exposure to toxic substances and genetic issues.
How does lung cancer develop?
The lungs are the organs of the respiratory system that are responsible for delivering oxygen to the body and expelling carbon dioxide.
Cancer develops when something stimulates cell overgrowth and, if not diagnosed early, can metastasize and contaminate other tissues in the body.
Neoplasms that cause metastases in the lungs after developing tumors elsewhere in the body are not considered lung cancers.
What are the symptoms?

One of the reasons this type of cancer is lethal is because its symptoms are almost always not easy to identify.
At first, it may seem like a common respiratory disease, and patients usually treat it with the remedies that are prescribed in these cases.
Although the signs are more evident as the condition worsens, some patients have symptoms that risk being misinterpreted even by doctors.
The most worrying thing is that the longer the cancer is diagnosed, the more likely it is to grow and become an incurable disease.
Consequently, it is essential to know what the symptoms are and when to undergo a complete check-up:
- Feeling tired or tired
- Cough and throat irritation
- Sudden weight loss
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing
- Wheezing and chest pain
- Phlegm and secretions. Cough with blood
- Bone pain
- Obstruction of the superior vena cava
- Continued episodes of fever and predisposition to pneumonia
Symptoms of this type of cancer can vary depending on the patient and the severity of the disease.
In fact, some people do not have any symptoms and find out through a lung X-ray taken for other reasons.
How to prevent lung cancer?

Although cancer is a disease that cannot always be prevented, there are some healthy habits that reduce the risk.
Smokers are aware of the dangers they run and, therefore, it is up to them whether they develop this disease or not.
The best way to prevent this condition is to quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke as well.
A smoker’s risk of developing lung cancer is the same as a non-smoker 10 or 15 years after quitting smoking.
A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins and minerals, as well as regular physical activity, are other good habits to adopt to avoid lung cancer.