Vascular Dementia: How To Recognize It?
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia, after Alzheimer’s disease. It has an incidence that varies between 10 and 20% of cases.
Like all types of dementia, it consists of cognitive impairment. This expression refers to the loss or worsening of some mental faculties, such as memory, reason or behavior.
Vascular dementia occurs following brain injury due to cerebrovascular disease. Certain areas of the brain do not get the blood supply they need and end up deteriorating. In this article, we explain why it occurs, what its symptoms are and how to treat them.
What does vascular dementia consist of?
In order to diagnose vascular dementia, some basic requirements must be met. First, the dementia criteria. As we mentioned earlier, they are based on a deterioration of the mental faculties. To quantify them, doctors use various analyzes and questionnaires.
On the other hand, there must be evidence of a cerebrovascular disease. The latter can occur due to a history of vascular problems or symptoms detected by physical exploration.
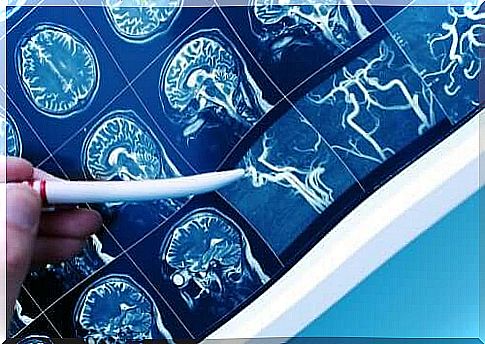
Techniques such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are also employed to observe possible brain injuries.
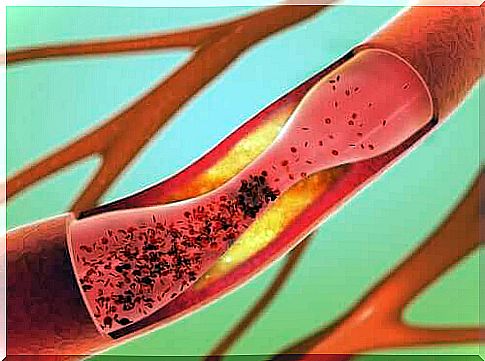
A cerebrovascular hemorrhage can be the cause of vascular dementia, but this is not always the case. In fact it can also occur due to other disorders that affect the blood vessels. Any condition that reduces blood flow in the brain, such as atherosclerosis, can be at the root of the problem.
For all these reasons we can identify certain risk factors. Having diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or smoking increases the risk of vascular dementia. In this sense, keeping these factors under control can reduce their incidence.

Symptoms
The symptoms of vascular dementia vary depending on which part of the brain the blood supply is least. They are similar to other forms of dementia.
First, the person in question may feel disoriented and have difficulty concentrating. The ability to organize thoughts is also reduced. One of the most alarming symptoms is memory loss.
Other common symptoms are:
- Unstable walking.
- Inability to control urine.
- Difficulty doing tasks that used to be done with ease.
- Speech disorders.
- Mood swings and personality.
- Loss of social skills.
- Depression.
- Disturbances in sleep.
- Possible hallucinations or delusions.
Symptoms may be clearer and more sudden when they occur following a cerebrovascular haemorrhage. In other cases, they can worsen according to obvious passages. This allows, in principle, to distinguish this pathology from Alzheimer’s, which is instead gradual.
However, even in this case the course can be gradual. As the disease progresses, symptoms become more evident and worsen. The patient with vascular dementia ends up being unable to take care of himself.
How to prevent vascular dementia?
Protecting the health of blood vessels is crucial. As we said earlier, maintaining adequate blood pressure must be one of the first measures. Furthermore, we must control or prevent diabetes. IS it is advisable to follow a good diet and exercise.
On the other hand, it is vital to quit smoking, as tobacco is harmful to blood vessels. At the same time, we need to keep cholesterol at moderate levels, as this reduces the risk of cerebrovascular hemorrhage. This is why diet is so important.
IS It is very important to pay attention to these preventive measures, as there is no effective therapy once vascular dementia is diagnosed. Treatment usually focuses on controlling risk factors.
How is vascular dementia diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made based on the likelihood that symptoms are triggered by a vascular problem. This probability increases according to personal history of cerebrovascular haemorrhage and any blood vessel or heart disorders.
Blood tests are also done to guide the diagnosis. The exam will focus, in particular, on the levels of cholesterol, sugar, anemia, etc. In addition, diagnostic imaging tests and ultrasound scans of the carotid arteries will be performed to assess their state of health.
Furthermore, neuropsychological tests help distinguish between the various types of dementia. They evaluate, for example, the ability to speak, write and work with numbers.
In addition, people with vascular dementia tend to find it more difficult to analyze a problem. However, they have less learning and information storage difficulties, as opposed to Alzheimer’s patients.
To conclude
To prevent vascular dementia, it is very important to lead a healthy lifestyle. Paying attention to your diet and exercising are two fundamental pillars. If despite these precautions you should notice alarming symptoms, do not hesitate to contact your doctor as soon as possible.